
Knee Osteotomy Surgeon in Denver Englewood
Individuals having arthritic conditions that are affecting only one side of the knee are candidates for knee osteotomy which involves removal or addition of a boner wedge either below or above the knee joint. Dr. Mayer provides diagnosis and knee osteotomy surgery in Denver Englewood. Dr. Mayer also provides highly specialized care during and after the surgery. Contact Dr. Mayer’s team for an appointment today!
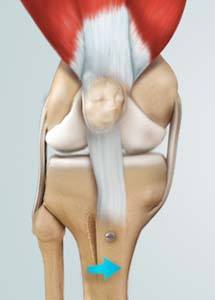
What is Knee Osteotomy?
Knee osteotomy is a surgical procedure in which the upper shinbone (tibia) or lower thighbone (femur) is cut and realigned. It is usually performed in arthritic conditions affecting only one side of your knee. The aim is to take the pressure off the damaged area and shift it to the other side of your knee with healthy cartilage. During the surgery, your surgeon will remove or add a wedge of bone either below or above the knee joint, depending on the site of arthritic damage.
Indications of Knee Osteotomy
Knee osteotomy is commonly indicated for osteoarthritis that is isolated to a single compartment (unicompartmental osteoarthritis).
Knee Osteotomy Procedure
A high tibial osteotomy is the most common type of osteotomy performed on arthritic knees. After general anesthesia is administered, your surgeon will map out the exact size of the bone wedge to be removed using an X-ray, CT scan or 3D computer modeling.
A four- to five-inch cut is made down in front of the knee, starting below the kneecap and running below the top of the shinbone. Guidewires are drilled from the lateral side to the top of the shinbone. A conventional oscillating saw is run along the guide wires and the bone wedge underneath the outside of the knee, below the healthy cartilage, is removed. The cartilage covering the top of the outside of the shinbone is left intact. Then, the top of the shinbone is reduced and fastened with surgical staples or screws. After the procedure is completed, the surgical site is then sutured usually with absorbable sutures and closed in layers.
Complications of Knee Osteotomy
Complications following high tibial osteotomy may include infection, skin necrosis, non-union (failure of the bones to heal), nerve injury, blood vessel injury, failure to correct the varus deformity, compartment syndrome, and deep vein thrombosis or blood clots.
If you would like to have additional information on knee treatments or would like to learn more about knee osteotomy, please contact the office of Dr. Mayer, serving the communities of Denver Englewood.
Related Topics
- Knee Arthroscopy
- ACL Reconstruction
- Knee Cartilage Restoration
- Meniscal Surgery
- Patellofemoral Knee Replacement
- Meniscus Replacement
- Cartilage Replacement
- PCL Reconstruction
- Knee Ligament Reconstruction
- Posterolateral Corner (PLC) Reconstruction
- Revision Knee Ligament Reconstruction
- Posterolateral Corner Reconstruction
- LCL Reconstruction
- MCL Reconstruction
- LPFL Reconstruction
- Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction
- Quadriceps Tendon Repair
- Knee Fracture Surgery
- Meniscectomy
- Distal Realignment Procedures
- Partial Arthroscopic Meniscectomy
- Patellofemoral Realignment
- Failed Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
- Failed Meniscus Repair
- Lateral Lengthening
- Meniscal Transplantation
- Prior Meniscectomy
- Tibial Eminence Fracture
- ORIF of the Knee Fracture
- Bone-Patellar Tendon-Bone (BPTB) Autograft
- Bone-Patellar Tendon-Bone (BPTB) Allograft
- Hamstring Autograft
- Hamstring Allograft
- Knee Osteotomy
- High Tibial Osteotomy
- Tibial Tubercle Osteotomy
- Distal Femoral Osteotomy
- Multiligament Reconstruction of the Knee
- Patellar Tendon Repair
- Arthroscopic Reconstruction of the Knee for Ligament Injuries
- Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation
- Partial Meniscectomy
- Cartilage Microfracture
- Pharmacological Interventions for Knee Injuries
- Ultrasound-Guided Genicular Nerve Block
- Intraarticluar Knee Injection
- Viscosupplementation
- Physical Therapy for Knee








