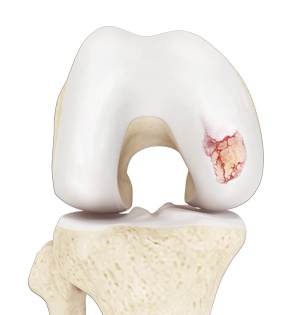
What is Knee Arthritis?
The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain-free movement in the joint. Arthritis is a general term covering numerous conditions where the joint surface or cartilage wears out. This surface can wear out for several reasons; often the definite cause is not known. Arthritis often affects the knee joint. When the articular cartilage wears out, the bone ends rub on one another and cause pain. The most common type of arthritis is osteoarthritis. It occurs with aging and use.
Causes of Knee Arthritis
There are numerous conditions that can cause arthritis but often the exact cause is never known. In general, but not always, it affects people as they get older (osteoarthritis). Other causes include:
- Trauma (fracture)
- Increased stress such as overuse and overweight
- Infection of the bone
- Connective tissue disorders
- Inactive lifestyle and obesity (overweight). Your weight is the single most important link between diet and arthritis, as being overweight puts an additional burden on your hips, knees, ankles, and feet.
- Inflammation (rheumatoid arthritis)
Symptoms of Knee Arthritis
Knee arthritis causes pain and decreased mobility of the knee joint. The cartilage lining is thinner than normal or completely absent. In the arthritic knee, there is an absent joint space that shows on X-ray. In the normal knee, there is a normal joint space. The capsule of the arthritic knee is swollen. The degree of cartilage damage and inflammation varies with the type and stage of arthritis. Bone spurs or excessive bone can also build up around the edges of the joint. The combinations of these factors make the arthritic knee stiff and limit activities due to pain or fatigue.
Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose knee arthritis with a medical history, a physical examination, and X-rays of the affected joint. During the physical examination, your doctor will examine the affected joint for swelling, pain, tenderness, and assess the joint’s range of motion. An X-ray of the knee may show a loss of the joint space and bone spur formation.
There is no blood test for knee arthritis.
Treatment
There is no known cure for knee arthritis. However, there are several treatments and lifestyle modifications that can help you ease your pain and symptoms. The objective of the treatment is to reduce pain, improve joint movement, and prevent further damage to the joint. The treatment of knee arthritis involves:
Medications: Medications may include different classes such as anti-inflammatory drugs, steroid injections, artificial joint fluid injections, and other drugs.
Lifestyle modifications
Some of the lifestyle modifications include:
- A moderate exercise program
- Use of heat or cold treatments
- Eating a healthy and well-balanced diet
- Getting adequate rest
- Losing weight
- Protecting your joints with the use of assistive devices such as splints or braces to support the weakened joints
- Physical therapy: Your physical therapist will teach you exercises to keep joints flexible and improve muscle strength.
- Surgery: Surgery is usually considered if non-surgical treatment fails to provide relief. Joint replacement surgery is considered as an option when the pain is so severe that it affects your ability to carry out normal activities.
Related Topics
- Patellar Instability
- Multiligament Instability
- Patellofemoral Instability
- Posterolateral Instability
- Knee Arthritis
- Knee Osteoarthritis
- Knee Injury
- Knee Pain
- Anterior Knee Pain
- Meniscal Tears
- Runners Knee
- Jumpers Knee
- Unstable Knee
- Knee Sprain
- MCL Sprains
- ACL Tears
- MCL Tears
- Meniscal Injuries
- PCL Injuries
- Ligament Injuries
- Knee Fracture
- Fractures of the Tibia
- Patella Fracture
- Tibial Shaft Fracture
- Kneecap Bursitis
- Chondral or Articular Cartilage Defects
- Quadriceps Tendon Rupture
- Patellar Tendon Rupture
- Lateral Meniscus Syndrome
- Osteonecrosis of the Knee
- Knee Angular Deformities
- Osteochondral Defect of the Knee
- Articular Cartilage Injury
- Goosefoot Bursitis of the Knee
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome
- Bowed Legs
- Recurrent Patella Dislocation
- Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee
- Chondromalacia Patella
- Patellar Tendinitis
- Knee Sports Injuries
- Multiligament Knee Injuries
- Women and ACL Injuries
- Medial Meniscus Syndrome
- Tibial Plateau Fracture
- Tibial Eminence Fractures
- Loose Bodies in the Knee
- Osgood Schlatter Disease
- Patellar Dislocation/Patellofemoral Dislocation








