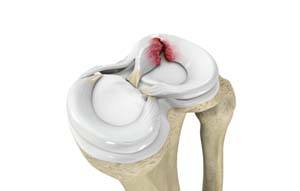
What is Meniscus?
There are two wedge-shaped cartilage pieces present between the thighbone and the shinbone each called a meniscus. The menisci stabilize the knee joint and act as shock absorbers.
What is a Meniscal Tear?
A meniscal tear is a common knee injury in athletes, especially those involved in contact sports. A sudden bend or twist in your knee causes the meniscus to tear. Elderly people are more prone to degenerative meniscal tears as the cartilage wears out and weakens with age.
Symptoms of Meniscal Tears
A torn meniscus causes pain, swelling, stiffness, or catching or locking sensation in your knee, making you unable to move your knee through its complete range of motion.
Diagnosis of Meniscal Tears
Your surgeon will examine your knee and evaluate your symptoms and medical history before suggesting a treatment plan.
Treatment of Meniscal Tears
The treatment depends on the type, size, and location of the tear, as well your age and activity level. If the tear is small with damage only in the outer edge of the meniscus, non-surgical treatment may be sufficient. However, if the symptoms do not resolve with non-surgical treatment, surgical treatment may be recommended.
Surgical Treatment for Meniscal Tears
Knee arthroscopy is a commonly recommended surgical procedure for meniscal tears.
Surgery can be performed using arthroscopy where a very small camera will be inserted through a very small incision to enable your surgeon to view the inside of your knee on a large screen. The surgery will be performed through other small incisions.
The surgical techniques include meniscus removal (meniscectomy), meniscus repair, and meniscus replacement. During meniscectomy, small instruments called shavers or scissors may be used to remove the torn meniscus. In arthroscopic meniscus repair, the torn meniscus will be pinned or sutured depending on the extent of the tear. Meniscus replacement or transplantation involves the replacement of a torn cartilage with the cartilage obtained from a donor or a cultured patch obtained from a laboratory. It is considered as a treatment option to relieve knee pain if you have undergone meniscectomy.
Related Topics
- Patellar Instability
- Multiligament Instability
- Patellofemoral Instability
- Posterolateral Instability
- Knee Arthritis
- Knee Osteoarthritis
- Knee Injury
- Knee Pain
- Anterior Knee Pain
- Meniscal Tears
- Runners Knee
- Jumpers Knee
- Unstable Knee
- Knee Sprain
- MCL Sprains
- ACL Tears
- MCL Tears
- Meniscal Injuries
- PCL Injuries
- Ligament Injuries
- Knee Fracture
- Fractures of the Tibia
- Patella Fracture
- Tibial Shaft Fracture
- Kneecap Bursitis
- Chondral or Articular Cartilage Defects
- Quadriceps Tendon Rupture
- Patellar Tendon Rupture
- Lateral Meniscus Syndrome
- Osteonecrosis of the Knee
- Knee Angular Deformities
- Osteochondral Defect of the Knee
- Articular Cartilage Injury
- Goosefoot Bursitis of the Knee
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome
- Bowed Legs
- Recurrent Patella Dislocation
- Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee
- Chondromalacia Patella
- Patellar Tendinitis
- Knee Sports Injuries
- Multiligament Knee Injuries
- Women and ACL Injuries
- Medial Meniscus Syndrome
- Tibial Plateau Fracture
- Tibial Eminence Fractures
- Loose Bodies in the Knee
- Osgood Schlatter Disease
- Patellar Dislocation/Patellofemoral Dislocation








